Fascism rises in europe answer key – Fascism Rises in Europe: A Comprehensive Guidedelves into the historical context, key characteristics, social impact, international implications, and legacy of fascism in Europe. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of this complex ideology, its rise and fall, and its enduring influence on contemporary society.
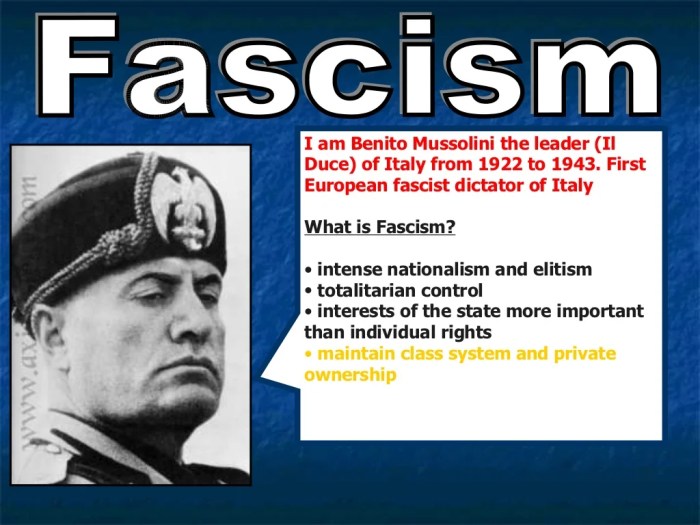
Fascism emerged in Europe in the aftermath of World War I, fueled by economic instability, social unrest, and a crisis of faith in traditional political systems. Fascist movements emphasized nationalism, authoritarianism, and a belief in the superiority of one’s own nation or race.
Historical Context: Fascism Rises In Europe Answer Key

The rise of fascism in Europe was a complex phenomenon with deep historical roots. Following the devastation of World War I, many European countries faced economic instability, political turmoil, and a loss of faith in traditional institutions. This created fertile ground for the growth of radical ideologies, including fascism.
Fascism, as an ideology, emphasized extreme nationalism, authoritarianism, and the glorification of violence. It appealed to those who felt disillusioned with the liberal democratic order and yearned for a sense of national unity and purpose.
Key Characteristics of Fascism
Fascism is characterized by several core principles:
- Extreme Nationalism:Fascism emphasizes the superiority of one’s own nation and promotes a sense of national pride and unity.
- Authoritarianism:Fascism rejects democratic principles and favors a strong, centralized government led by a charismatic leader.
- Militarism:Fascism glorifies military strength and promotes the use of violence to achieve political goals.
- Anti-Intellectualism:Fascism distrusts intellectualism and critical thinking, favoring emotional appeals and simplistic slogans.
- Economic Interventionism:Fascist governments often intervene in the economy to control production and allocate resources.
Impact on Society, Fascism rises in europe answer key
Fascism had a profound impact on European society. It suppressed political opposition, curtailed civil liberties, and promoted a cult of personality around the leader.
Fascist regimes also implemented policies that discriminated against minorities, women, and workers. Jews, Roma, and other minority groups faced persecution and violence.
Fascist propaganda played a crucial role in shaping public opinion. It glorified the nation and the leader, demonized enemies, and suppressed dissenting voices.
International Implications
Fascism had significant international implications. It contributed to the outbreak of World War II and influenced the development of other totalitarian regimes.
Fascist Italy and Nazi Germany formed an alliance and invaded neighboring countries, leading to a global conflict. Fascist ideology also inspired regimes in Spain, Portugal, and Japan.
Legacy of Fascism
Fascism declined after World War II, but its legacy continues to influence contemporary politics and society.
Neo-fascist and far-right movements have emerged in various countries, promoting xenophobia, nationalism, and authoritarianism.
The rise of fascism serves as a reminder of the dangers of extremism and the importance of defending democratic values.
Clarifying Questions
What are the key characteristics of fascism?
Fascism is characterized by extreme nationalism, authoritarianism, a belief in the superiority of one’s own nation or race, and the suppression of individual rights and freedoms.
How did fascism impact society?
Fascism had a profound impact on society, leading to the suppression of dissent, the persecution of minorities, and the erosion of democratic institutions.
What was the role of fascism in World War II?
Fascist regimes played a significant role in the outbreak and prosecution of World War II, with Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy being the primary aggressors.